Communication and Deployment Biases¶
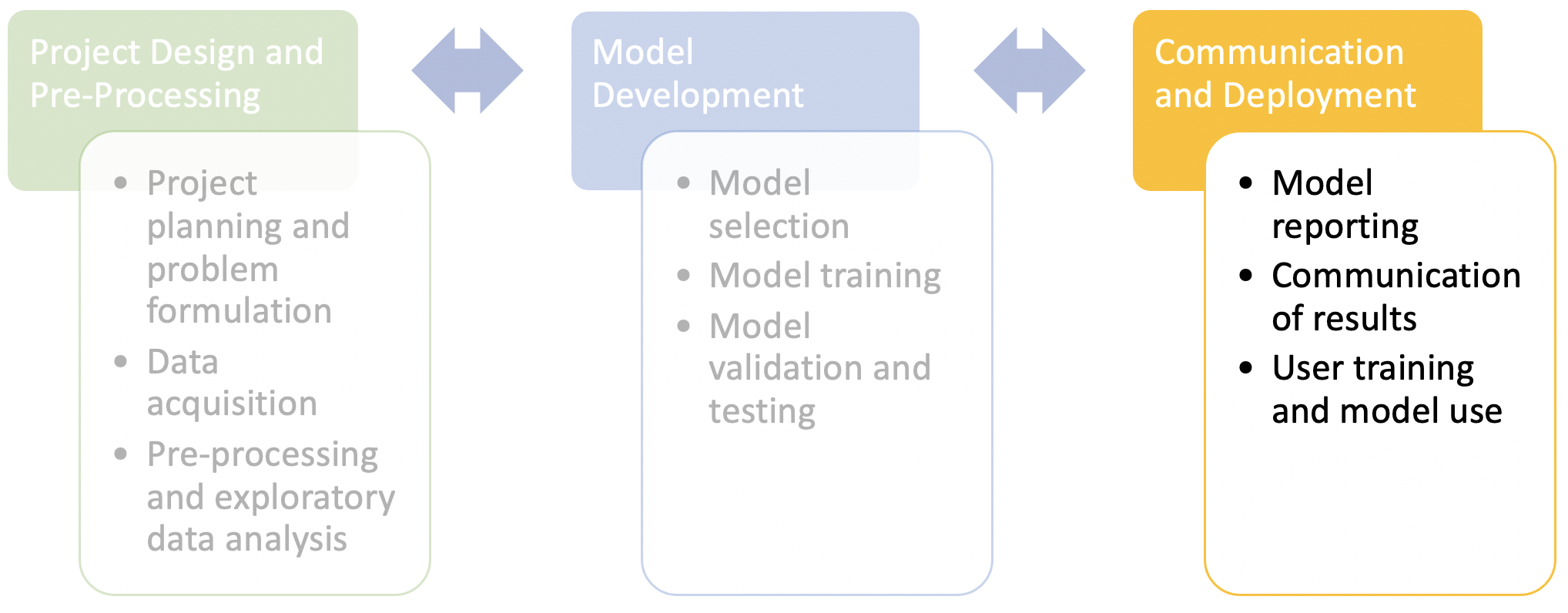
Fig. 5 A simplified schematic of a project worklow.¶
Deployment Bias¶
Definition
Deployment bias refers, generally, to any bias that arises during deployment, where a system is used or interpreted in inappropriate ways, perhaps not intended by the designers or developers. This can subsume the effects of biases such as ‘training-serving skew’ that arise earlier in the workflow, but also extends to biases that emerge from the misuse of the system or model.
Deliberative Prompts
Have you consulted with relevant stakeholder groups to identify and understand the potential impacts of human factors within the context or environment of your model or system’s use?
Related biases: Training-Serving Skew, Automation Bias
Automation Bias¶
Definition
Automation bias refers to a psychological phenomenon that can occur when users (e.g. healthcare professionals) of a model (or decision support system) are unaware of the model’s accuracy or unable to appropriately assess the reliability of a model’s predictions. As such they can a) become over-reliant on the tool and trust the system too much, in turn failing to identify inaccurate predictions or classifications, or b) become suspicious of the model and under-use it, despite the fact that it may outperform on tasks like risk assessment.
Deliberative Prompts
Have you considered requirements such as transparency or interpretability when designing your model?
Does the intended use domain demand a greater need for interpretability, and how may this affect the model’s accuracy (e.g. reducing model complexity)?
Related biases: Dismissal Bias
Dismissal Bias¶
Definition
Closely related to automation bias, dismissal bias refers to a narrower psychological phenomenon that arises when a decision support tool systematically delivers incorrect alerts for a protected group (e.g. early warning scores), leading to a desensitisation to those alerts—otherwise known as ‘alert fatigue’.
Deliberative Prompts
What steps have you taken to evaluate and measure the performance of your model across (protected) sub-groups of the population? What measure of fairness have you adopted for this purpose?
Is your model likely to be implemented within a system that alerts or notifies users (e.g. early warning system)? If so, have you considered the necessary human factors (e.g. usability, interpretability, explainability)?
Related biases: Automation Bias
Biases of Rhetoric or Spin¶
Definition
A group of related biases that refer to the use of persuasive techniques, opinions, or modes of argumentation that steer the reader to adopt a particular belief, attitude, or policy, which is not sufficiently justifiable on the basis of the evidence. Put another way, such biases systematically mislead readers into viewing the results of a study in a more favourable (or unfavourable) light. These biases may be more prevalent in “popular” or “fashionable” topics, where there may be additional incentives to oversell the impact of the study
Deliberative Prompts
Are there methods of internal peer review (or “red teams”) that you can use to proactively identify cases where you are going too far beyond what is justifiably implied by the data?
Related biases: Positive results Bias
Positive results Bias¶
Definition
Arises due to a systematic favouring of positive results, rather than negative (or non-significant) results. This bias can be exacerbated by the authors of the study, during the submission stage, as well as the peer reviewers and journal editors when making decisions about whether to publish articles or reports. A notable concern here is that the non-publication of valuable (replication or reproduction) studies that disconfirm previous studies, can lead to unnecessary redundancy in research activities as groups may continue to replicate studies that do not need to be performed.
Deliberative Prompts
Have you sufficiently reported all relevant results of the study, even if they speak against your favoured hypothesis?
If your study is not accepted in your favoured journal, have you made provisions to ensure that the results can be accessed through other repositories or services that promote open science principles?
Related biases: Biases of Rhetoric or Spin, Confirmation Bias
