MLJ Cheatsheet
Starting an interactive MLJ session
julia> using MLJjulia> MLJ_VERSION # version of MLJ for this cheatsheetv"0.20.3"
Model search and code loading
info("PCA") retrieves registry metadata for the model called "PCA"
info("RidgeRegressor", pkg="MultivariateStats") retrieves metadata for "RidgeRegresssor", which is provided by multiple packages
doc("DecisionTreeClassifier", pkg="DecisionTree") retrieves the model document string for the classifier, without loading model code
models() lists metadata of every registered model.
models("Tree") lists models with "Tree" in the model or package name.
models(x -> x.is_supervised && x.is_pure_julia) lists all supervised models written in pure julia.
models(matching(X)) lists all unsupervised models compatible with input X.
models(matching(X, y)) lists all supervised models compatible with input/target X/y.
With additional conditions:
models() do model
matching(model, X, y) &&
model.prediction_type == :probabilistic &&
model.is_pure_julia
endTree = @load DecisionTreeClassifier pkg=DecisionTree imports "DecisionTreeClassifier" type and binds it to Tree tree = Tree() to instantiate a Tree.
tree2 = Tree(max_depth=2) instantiates a tree with different hyperparameter
Ridge = @load RidgeRegressor pkg=MultivariateStats imports a type for a model provided by multiple packages
For interactive loading instead, use @iload
Scitypes and coercion
scitype(x) is the scientific type of x. For example scitype(2.4) == Continuous
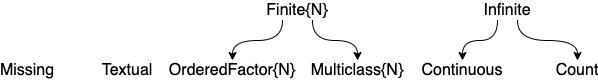
| type | scitype |
|---|---|
AbstractFloat | Continuous |
Integer | Count |
CategoricalValue and CategoricalString | Multiclass or OrderedFactor |
AbstractString | Textual |
Figure and Table for common scalar scitypes
Use schema(X) to get the column scitypes of a table X
coerce(y, Multiclass) attempts coercion of all elements of y into scitype Multiclass
coerce(X, :x1 => Continuous, :x2 => OrderedFactor) to coerce columns :x1 and :x2 of table X.
coerce(X, Count => Continuous) to coerce all columns with Count scitype to Continuous.
Ingesting data
Split the table channing into target y (the :Exit column) and features X (everything else), after a seeded row shuffling:
using RDatasets
channing = dataset("boot", "channing")
y, X = unpack(channing, ==(:Exit); rng=123)Same as above but exclude :Time column from X:
using RDatasets
channing = dataset("boot", "channing")
y, X = unpack(channing,
==(:Exit), # y is the :Exit column
!=(:Time); # X is the rest, except :Time
rng=123)Splitting row indices into train/validation/test, with seeded shuffling:
train, valid, test = partition(eachindex(y), 0.7, 0.2, rng=1234) for 70:20:10 ratio
For a stratified split:
train, test = partition(eachindex(y), 0.8, stratify=y)
Split a table or matrix X, instead of indices:
Xtrain, Xvalid, Xtest = partition(X, 0.5, 0.3, rng=123)
Getting data from OpenML:
table = OpenML.load(91)
Creating synthetic classification data:
X, y = make_blobs(100, 2) (also: make_moons, make_circles)
Creating synthetic regression data:
X, y = make_regression(100, 2)
Machine construction
Supervised case:
model = KNNRegressor(K=1) and mach = machine(model, X, y)
Unsupervised case:
model = OneHotEncoder() and mach = machine(model, X)
Fitting
fit!(mach, rows=1:100, verbosity=1, force=false) (defaults shown)
Prediction
Supervised case: predict(mach, Xnew) or predict(mach, rows=1:100)
Similarly, for probabilistic models: predict_mode, predict_mean and predict_median.
Unsupervised case: transform(mach, rows=1:100) or inverse_transform(mach, rows), etc.
Inspecting objects
@more gets detail on the last object in REPL
params(model) gets a nested-tuple of all hyperparameters, even nested ones
info(ConstantRegressor()), info("PCA"), info("RidgeRegressor", pkg="MultivariateStats") gets all properties (aka traits) of registered models
info(rms) gets all properties of a performance measure
schema(X) get column names, types and scitypes, and nrows, of a table X
scitype(X) gets the scientific type of X
fitted_params(mach) gets learned parameters of the fitted machine
report(mach) gets other training results (e.g. feature rankings)
Saving and retrieving machines using Julia serializer
MLJ.save("trained_for_five_days.jls", mach) to save machine mach (without data)
predict_only_mach = machine("trained_for_five_days.jlso") to deserialize.
Performance estimation
evaluate(model, X, y, resampling=CV(), measure=rms, operation=predict, weights=..., verbosity=1)
evaluate!(mach, resampling=Holdout(), measure=[rms, mav], operation=predict, weights=..., verbosity=1)
evaluate!(mach, resampling=[(fold1, fold2), (fold2, fold1)], measure=rms)
Resampling strategies (resampling=...)
Holdout(fraction_train=0.7, rng=1234) for simple holdout
CV(nfolds=6, rng=1234) for cross-validation
StratifiedCV(nfolds=6, rng=1234) for stratified cross-validation
TimeSeriesSV(nfolds=4) for time-series cross-validation
or a list of pairs of row indices:
[(train1, eval1), (train2, eval2), ... (traink, evalk)]
Tuning
Tuning model wrapper
tuned_model = TunedModel(model=…, tuning=RandomSearch(), resampling=Holdout(), measure=…, operation=predict, range=…)
Ranges for tuning (range=...)
If r = range(KNNRegressor(), :K, lower=1, upper = 20, scale=:log)
then Grid() search uses iterator(r, 6) == [1, 2, 3, 6, 11, 20].
lower=-Inf and upper=Inf are allowed.
Non-numeric ranges: r = range(model, :parameter, values=…)
Nested ranges: Use dot syntax, as in r = range(EnsembleModel(atom=tree), :(atom.max_depth), ...)
Can specify multiple ranges, as in range=[r1, r2, r3]. For more range options do ?Grid or ?RandomSearch
Tuning strategies
RandomSearch(rng=1234) for basic random search
Grid(resolution=10) or Grid(goal=50) for basic grid search
Also available: LatinHyperCube, Explicit (built-in), MLJTreeParzenTuning, ParticleSwarm, AdaptiveParticleSwarm (3rd-party packages)
Learning curves
For generating a plot of performance against parameter specified by range:
curve = learning_curve(mach, resolution=30, resampling=Holdout(), measure=…, operation=predict, range=…, n=1)
curve = learning_curve(model, X, y, resolution=30, resampling=Holdout(), measure=…, operation=predict, range=…, n=1)
If using Plots.jl:
plot(curve.parameter_values, curve.measurements, xlab=curve.parameter_name, xscale=curve.parameter_scale)
Controlling iterative models
Requires: using MLJIteration
iterated_model = IteratedModel(model=…, resampling=Holdout(), measure=…, controls=…, retrain=false)
Controls
Increment training: Step(n=1)
Stopping: TimeLimit(t=0.5) (in hours), NumberLimit(n=100), NumberSinceBest(n=6), NotANumber(), Threshold(value=0.0), GL(alpha=2.0), PQ(alpha=0.75, k=5), Patience(n=5)
Logging: Info(f=identity), Warn(f=""), Error(predicate, f="")
Callbacks: Callback(f=mach->nothing), WithNumberDo(f=n->@info(n)), WithIterationsDo(f=i->@info("num iterations: $i")), WithLossDo(f=x->@info("loss: $x")), WithTrainingLossesDo(f=v->@info(v))
Snapshots: Save(filename="machine.jlso")
Wraps: MLJIteration.skip(control, predicate=1), IterationControl.with_state_do(control)
Performance measures (metrics)
Do measures() to get full list.
info(rms) to list properties (aka traits) of the rms measure
Transformers
Built-ins include: Standardizer, OneHotEncoder, UnivariateBoxCoxTransformer, FeatureSelector, FillImputer, UnivariateDiscretizer, ContinuousEncoder, UnivariateTimeTypeToContinuous
Externals include: PCA (in MultivariateStats), KMeans, KMedoids (in Clustering).
models(m -> !m.is_supervised) to get full list
Ensemble model wrapper
EnsembleModel(atom=…, weights=Float64[], bagging_fraction=0.8, rng=GLOBAL_RNG, n=100, parallel=true, out_of_bag_measure=[])
Target transformation wrapper
TransformedTargetModel(model=ConstantClassifier(), target=Standardizer())
Pipelines
pipe = (X -> coerce(X, :height=>Continuous)) |> OneHotEncoder |> KNNRegressor(K=3)
Unsupervised:
pipe = Standardizer |> OneHotEncoder
Concatenation:
pipe1 |> pipe2 or model |> pipe or pipe |> model, etc
Define a supervised learning network:
Xs = source(X) ys = source(y)
... define further nodal machines and nodes ...
yhat = predict(knn_machine, W, ys) (final node)
Exporting a learning network as a stand-alone model:
Supervised, with final node yhat returning point predictions:
@from_network machine(Deterministic(), Xs, ys; predict=yhat) begin
mutable struct Composite
reducer=network_pca
regressor=network_knn
endHere network_pca and network_knn are models appearing in the learning network.
Supervised, with yhat final node returning probabilistic predictions:
@from_network machine(Probabilistic(), Xs, ys; predict=yhat) begin
mutable struct Composite
reducer=network_pca
classifier=network_tree
endUnsupervised, with final node Xout:
@from_network machine(Unsupervised(), Xs; transform=Xout) begin
mutable struct Composite
reducer1=network_pca
reducer2=clusterer
end
endUnivariateTimeTypeToContinuous